The two most popular surface treatments in the world of manufacturing are Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating and powder coating. While both are used to protect and enhance products, they achieve this through fundamentally different processes, resulting in very different properties and applications.
This blog explores the key differences between PVD and powder coating, helping you determine which is the best surface treatment for your specific requirements.
1. Process: Wet vs. Vacuum
The core difference lies in the application method—one is a dry, thermal process, and the other is a high-tech, vacuum-based process.

2. Properties & Performance
The differences in the process lead to a stark contrast in the final coating properties, especially in terms of strength and thinness.
PVD Coating: The High-Performance Thin Film
PVD coatings are renowned for creating an extremely thin film—ranging from 0.5 to 5 microns (significantly thinner than a human hair)—that is chemically bonded to the substrate at the atomic level.
- Superior Hardness: PVD films, like Titanium Nitride (TiN), are exceptionally hard, often 3 to 5 times harder than the substrate itself, providing industry-leading wear resistance.
- Corrosion Resistance: The coating is dense and non-porous, forming a true barrier that offers outstanding corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments.
- Low Friction: Many PVD coatings offer low-friction properties, which is ideal for cutting tools, molds, and mechanical components.
Powder Coating: The Durable, Thick Layer
Powder coating is much thicker, typically ranging from 25 to 125 microns. It creates a robust, protective shell around the part.
- Impact Resistance: Due to its thickness and polymer base, it provides excellent resistance to chipping, scratching, and general impact.
- Aesthetic Versatility: It is highly valued for its wide range of color, texture, and gloss options, making it a favorite for decorative finishes.
UV Resistance: Certain powder coating formulations (like Polyester) offer excellent resistance to UV light and weathering, making them ideal for outdoor equipment and architectural panels.
3. Applications and Cost-Effectiveness
The specific benefits of each coating dictate its ideal applications and overall cost-effectiveness.
Where PVD Excels
PVD coating is the choice for high-precision, high-stress, and high-performance applications where superior function is the priority.
- Cutting Tools (Drills, End Mills) & Molds
- Medical devices (Implants, Surgical Tools)
- Automotive and Aerospace Components
- High-End Decorative Finishes (Watches, luxury fixtures)
Cost & Value: PVD has a higher initial cost due to the complex, specialized equipment required. However, the long-term value from a 5x increase in tool life often makes it the more cost-effective solution over the product’s lifespan.
Where Powder Coating Excels
Powder coating is the preferred choice for larger surface areas and high-volume consumer/industrial goods where a thick, aesthetically pleasing, and durable finish is needed.
- Outdoor Furniture & Fences
- Home Appliances (Refrigerators, Washers)
- Automotive Chassis & Wheel Rims
- Architectural Elements and General Fabrication
Cost & Value: Powder coating is significantly less expensive and easier to scale for large production runs, making it the more budget-friendly option for non-critical, aesthetic, and corrosion-protection purposes.
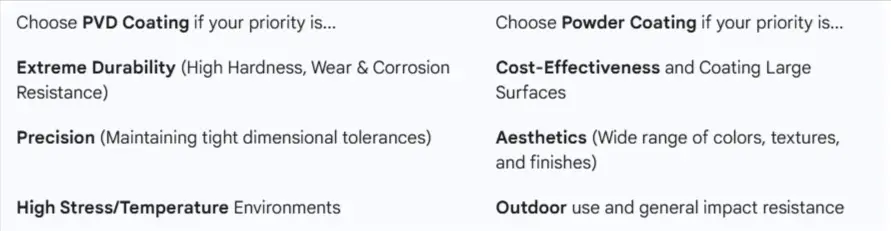
Choosing the Right Solution
The decision between PVD coating and powder coating depends entirely on the job’s specific requirements:
For clients seeking advanced PVD coating solutions that deliver precision and exceptional quality in high-demand environments, ARKA PVD offers the technical expertise to ensure your tools and components perform better and last longer.

 PVD Coating
PVD Coating
What Is PVD Coating? Guide To Physical Vapor Deposition In India
October 31, 2025 12:39 pm[…] Read MoreDifference between PVD and Powder Coating? […]
PVD Coating For Industrial Components In India | ARKA PVD
November 14, 2025 6:04 am[…] Difference between PVD and Power coating? […]
How TiN (Titanium Nitride) Coating Extends The Life Of Cutting Tools
November 20, 2025 5:06 pm[…] Read more: Difference Between PVD and Powder Coating […]